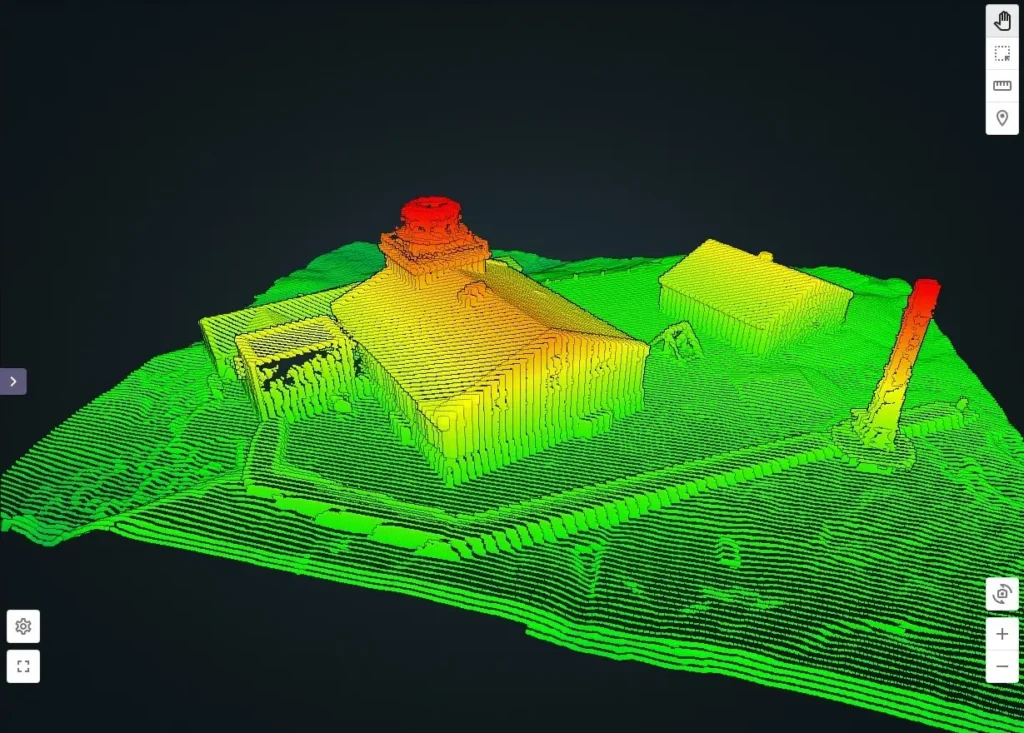
A LiDAR scanner is an advanced laser-based device used for capturing high-precision 3D data of surfaces, landscapes, and objects. It plays a crucial role in geospatial mapping, surveying, and environmental analysis. Unlike traditional surveying methods, a LiDAR scanner emits laser pulses that measure distances accurately, generating detailed point cloud data. This technology is widely used in industries such as construction, forestry, archaeology, and urban planning.
If you work with LiDAR scanning technology, ensuring seamless data sharing and processing is essential. SurveyTransfer provides an efficient solution for managing and sharing LiDAR scanner datasets securely. In this article, we’ll explore how LiDAR scanners work, their different types, key applications, and how to manage LiDAR data efficiently.
How Does a LiDAR Scanner Work?
A LiDAR scanner works by emitting laser pulses toward a target surface. These pulses reflect back to the sensor, and the time taken for their return is used to calculate precise distances. This data is then processed to create 3D models, terrain maps, and point cloud datasets.
Key Steps in LiDAR Scanning:
- Laser Emission – The scanner emits rapid laser pulses.
- Reflection Capture – The laser pulses hit surfaces and bounce back.
- Distance Calculation – The system calculates distances based on light travel time.
- Data Processing – The scanner compiles a dense point cloud dataset.
- 3D Model Generation – The collected data is converted into 3D digital terrain models (DTM) or elevation models (DEM).
LiDAR scanners can be mounted on various platforms, including airborne drones, vehicles, and stationary tripods.
Types of LiDAR Technology
Not all LiDAR scanners are the same. There are several types, each suited for different applications.

1. Airborne (Aerial) LiDAR Scanners
Airborne LiDAR scanners are mounted on drones, airplanes, or helicopters to capture large-scale terrain data. They are commonly used for forestry, environmental mapping, and flood modeling.
2. Terrestrial (Ground-Based) LiDAR Scanners
These scanners are stationary or vehicle-mounted and used for architectural scanning, urban development, and infrastructure projects. Ground-based LiDAR is ideal for capturing detailed 3D building structures.
3. Mobile LiDAR Scanners
Mounted on vehicles, mobile LiDAR scanners are widely used for city mapping, transportation planning, and infrastructure monitoring. This type allows for real-time data collection over large distances.
Applications of LiDAR Scanner
LiDAR scanners are transforming various industries by providing highly accurate geospatial data. Here are some of the key applications:
1. Surveying and Mapping
LiDAR scanners create precise topographic maps, making them essential for land surveying, real estate, and property boundary determination.
2. Forestry and Environmental Monitoring
Forestry professionals use LiDAR scanners to analyze tree canopy heights, vegetation density, and ecosystem changes. Environmental scientists also use LiDAR for tracking soil erosion and flood risk assessment.
3. Construction and Urban Planning
Construction engineers use LiDAR scanners to create 3D site models, assess terrain conditions, and monitor progress. Urban planners rely on LiDAR data for road network analysis and city development projects.
4. Archaeology and Historical Preservation
Archaeologists utilize LiDAR scanners to uncover hidden ruins, map excavation sites, and document ancient structures with unparalleled precision.
LiDAR Scanner vs. Photogrammetry – Which One Should You Use?
A common question is whether to use LiDAR scanning or photogrammetry. Both have unique benefits depending on project needs.
| Feature | LiDAR Scanner | Photogrammetry |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High (centimeter-level) | Moderate (depends on resolution) |
| Works in Low Light | Yes | No |
| Ideal for Dense Vegetation | Yes | No |
| Data Output | 3D Point Cloud | 2D and 3D Models |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
LiDAR scanners excel in capturing fine details, even through dense vegetation, while photogrammetry is a more budget-friendly option for aerial and landscape modeling.
How to Process LiDAR Scanner Data?
Once LiDAR scanner data is collected, it must be processed effectively. Here’s how:
- Noise Filtering – Remove unnecessary data points to enhance clarity.
- Classification – Categorize features like trees, buildings, and ground elevation.
- DEM & DTM Creation – Convert raw point clouds into digital models.
- 3D Visualization – Use software to render interactive terrain maps.
- Data Sharing – Upload to platforms like SurveyTransfer for team collaboration.
Efficient data sharing ensures smooth project execution, especially in large-scale mapping operations.
Share and Manage LiDAR Scanner Data with SurveyTransfer
Handling large LiDAR scanner datasets can be challenging, especially for teams that need seamless collaboration. SurveyTransfer offers a powerful solution for:
- Cloud-Based Storage – Securely store and access LiDAR data from anywhere.
- Easy Data Sharing – Share LiDAR scanner point clouds with team members effortlessly.
- Efficient Processing – Organize and manage large datasets without complexity.
Whether you’re using aerial, mobile, or ground-based LiDAR scanners, SurveyTransfer simplifies data handling so you can focus on analysis and project execution.
Conclusion: The Power of LiDAR Scanners in 3D Mapping
A LiDAR scanner is a crucial tool for surveying, mapping, and geospatial data collection. With applications in construction, forestry, archaeology, and urban planning, LiDAR scanning technology continues to revolutionize spatial data analysis.
Ready to streamline your LiDAR workflow? Get started with SurveyTransfer now!
If you really liked what you read than you can share it with your friends. 🙂
Did you like what you read? Do you want to read similar ones?