LiDAR technology is revolutionizing how we capture and analyze spatial data, offering unprecedented accuracy and detail. But what exactly is LiDAR, and how does it work? This blog dives into the fundamentals of this 3D mapping technology, its real-world applications, and how SurveyTransfer can help you manage and share your datasets with ease.
What Is LiDAR?
LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances. By calculating the time it takes for a laser pulse to travel to an object and back, LiDAR systems can create highly accurate 3D models of surfaces and objects. This technology captures spatial data in remarkable detail, making it invaluable for industries that rely on precision mapping and modeling.
LiDAR’s ability to generate accurate, high-resolution elevation data makes it a powerful tool for scientists, engineers, and businesses worldwide.
How Does LiDAR Work?
LiDAR operates by emitting thousands of laser pulses per second from a sensor. These pulses reflect off surfaces, and the system calculates the time taken for each pulse to return. This process creates a point cloud—a detailed collection of 3D points that represent the scanned environment.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how LiDAR works:
- Laser Pulse Emission: The sensor releases laser beams toward the target area.
- Reflection from Surfaces: The laser pulses bounce back after hitting objects or terrain.
- Distance Measurement: The system measures the time delay to determine the distance.
- Point Cloud Creation: The collected data points form a detailed 3D representation.
- Data Processing: Specialized software processes the data for visualization and analysis.
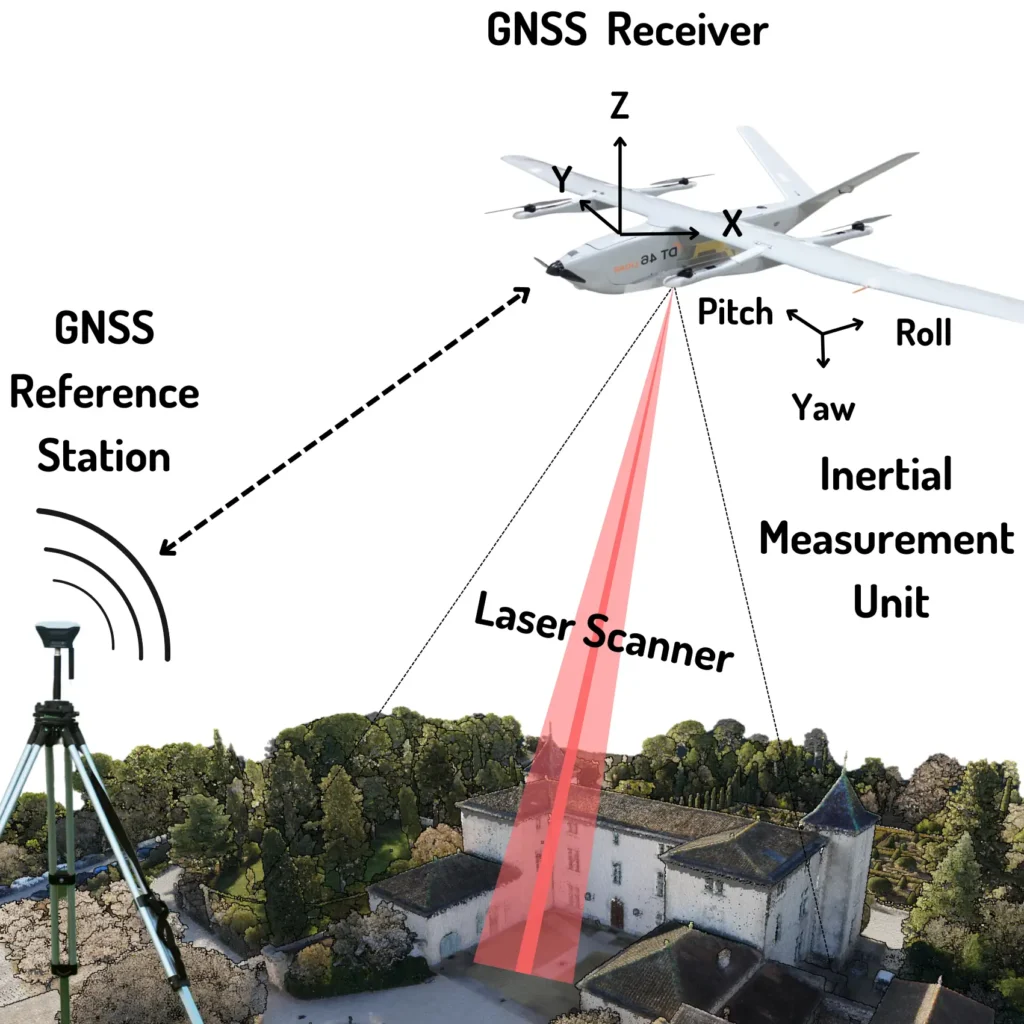
LiDAR systems can be mounted on various platforms:
- Aerial: Mounted on drones, helicopters, or planes for large-scale mapping.
- Ground-Based: Used for detailed scans of buildings, streets, or archaeological sites.
LiDAR Technology & Tools
LiDAR technology relies on advanced hardware and software to function effectively. The essential tools include:
- Laser Scanner: Emits and receives laser pulses.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Tracks the exact location of the sensor.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures orientation and movement of the device.
In terms of platforms:
- Drones and aircraft are commonly used for large-area scans.
- Ground vehicles and tripod-mounted systems help gather precise, close-range data.
Data processing software then interprets the point cloud data, generating detailed maps, 3D models, or digital elevation models (DEMs).
LiDAR Applications Across Industries
LiDAR technology has transformed multiple sectors by providing high-resolution spatial data. Here are some of its most impactful applications:
- Environmental Monitoring: Used for forest mapping, vegetation analysis, and erosion tracking.
- Urban Planning: Assists in infrastructure development, city planning, and smart city projects.
- Agriculture: Enables precision farming through detailed crop monitoring and land assessment.
- Disaster Management: Helps in flood modeling, landslide detection, and emergency response planning.
- Archaeology: Uncovers hidden structures and ancient sites buried under dense foliage.
The versatility and precision of LiDAR make it an invaluable asset across these diverse fields.

3D Mapping & Data Accuracy
One of the standout features of LiDAR is its ability to create highly accurate 3D maps using point cloud data. The precision of these maps depends on several factors:
- Spatial Resolution: The density of the point cloud affects the detail of the final model.
- Reflective Surfaces: Different materials reflect laser pulses in unique ways, affecting measurement reliability.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors like lighting and weather can influence data accuracy.
Thanks to its high-resolution data capture capabilities, LiDAR technology is trusted for applications that demand precise measurements and detailed terrain analysis.
Benefits of LiDAR Technology
LiDAR technology offers numerous advantages for professionals across various industries:
- High Accuracy: Provides precise measurements of terrain, structures, and objects.
- Efficient Data Collection: Gather large amounts of data quickly, even in challenging environments.
- Works in Low-Light Conditions: Can operate effectively in various lighting conditions.
- Versatility: Applicable across land, water, and air, making it suitable for diverse industries.
These benefits make LiDAR a preferred solution for tasks that require detailed spatial data and reliable measurement accuracy.
Seamlessly Share Map and 3D Data With SurveyTransfer
Managing and sharing large LiDAR datasets can be challenging—but that’s where SurveyTransfer comes in. Our platform simplifies map and 3D data sharing by offering:
- Secure Data Transfer: Safely share your high-resolution spatial data with team members and clients.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easily upload, manage, and share your LiDAR files.
- Collaboration Tools: Enable seamless cooperation among surveyors, engineers, and analysts.
If you’re looking for a hassle-free solution for sharing map and 3D data, SurveyTransfer offers the tools you need for efficient and secure data management.
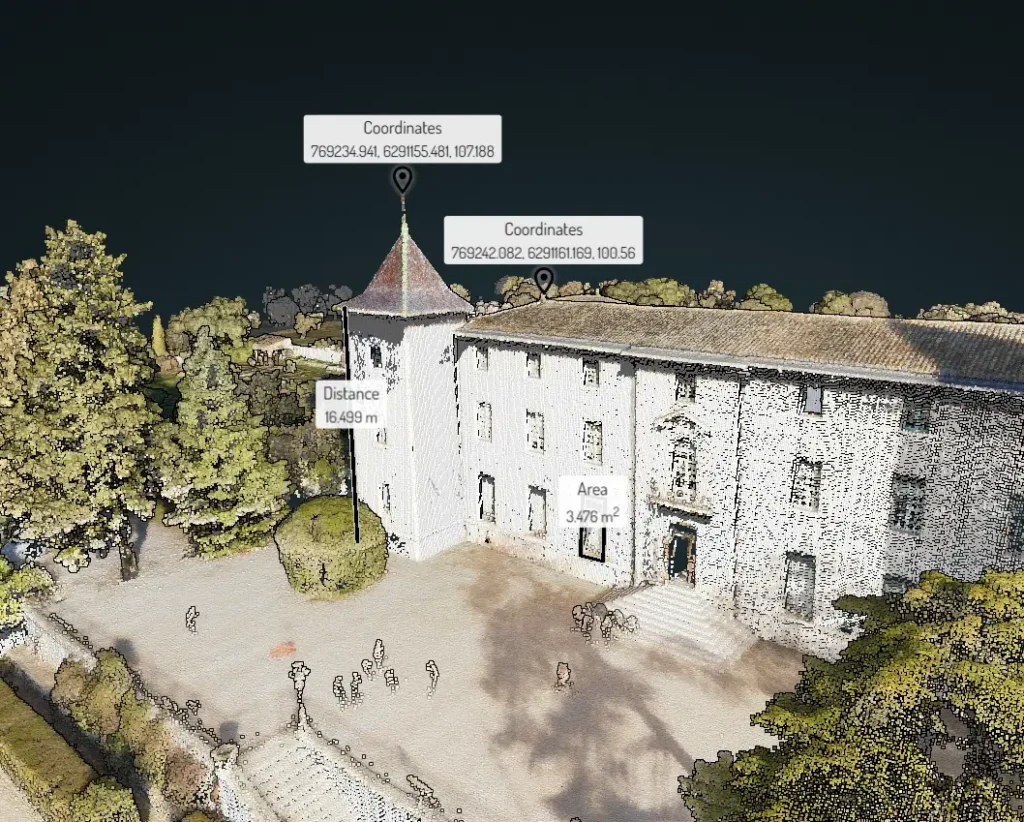

Summary
LiDAR technology is transforming industries by offering precise, high-resolution spatial data for mapping, monitoring, and analysis. From environmental monitoring to urban planning, LiDAR’s applications are vast and continually expanding.
With SurveyTransfer, sharing your valuable LiDAR data becomes effortless and secure—helping you unlock the full potential of your spatial data projects.
If you really liked what you read than you can share it with your friends. 🙂
Did you like what you read? Do you want to read similar ones?