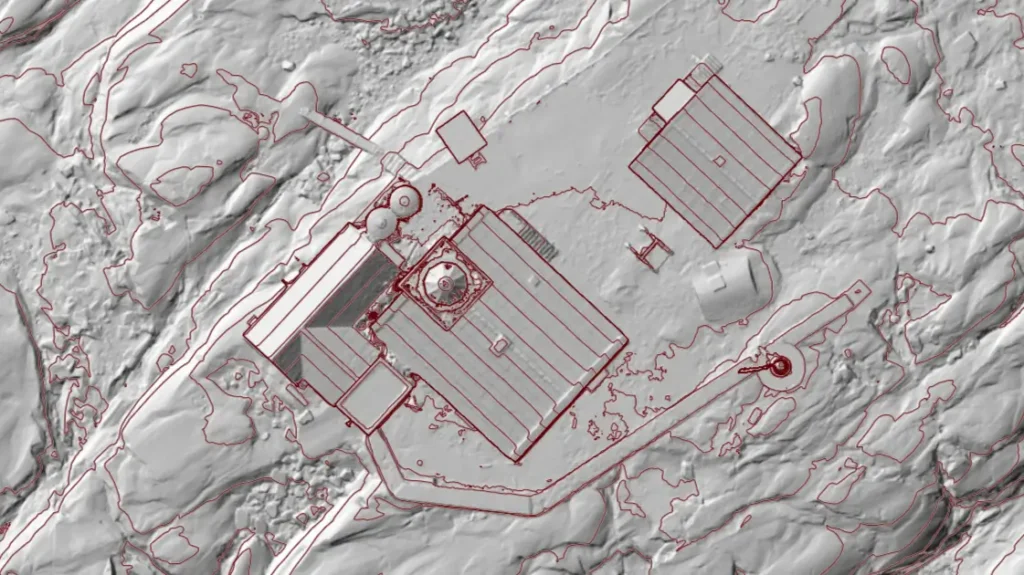
Digital Terrain Model (DTM) is essential in geospatial analysis, providing accurate representations of the Earth’s surface. Unlike Digital Surface Models (DSMs), which capture all objects like trees and buildings, DTMs focus solely on bare ground topography. These models play a crucial role in surveying, engineering, and environmental studies.
Understanding Digital Terrain Models (DTM)
A Digital Terrain Model is a three-dimensional representation of a landscape, generated from elevation data. Using LiDAR, photogrammetry, or satellite imagery, DTMs depict natural landforms by removing above-ground features. The resulting data helps in creating elevation profiles, contour maps, and hydrological models.
How DTM Differ from DSM and DEM
DTM, DSM, and Digital Elevation Models (DEM) are often confused. While DSM includes surface features like buildings and trees, DTM represents only the ground surface. DEM, on the other hand, serves as an umbrella term, encompassing both DTMs and DSMs. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for choosing the right model for geospatial applications.
| Feature | DTM (Digital Terrain Model) | DSM (Digital Surface Model) | DEM (Digital Elevation Model) |
| Definition | Represents the bare-earth surface without objects | Includes terrain and all above-ground features | A general term for elevation data (can be DTM or DSM) |
| Includes Vegetation & Buildings? | No | Yes | Sometimes |
| Use Cases | Hydrology, infrastructure planning, land surveying | Urban planning, forestry, telecommunication | General topographic analysis |
| Data Source | Lidar, photogrammetry, ground surveys | Lidar, satellite imagery, aerial photogrammetry | Various elevation data sources |
How DTM is Created
DTM is generated using advanced remote sensing techniques. LiDAR technology provides highly accurate elevation points, while photogrammetry extracts terrain data from overlapping images. Surveyors also use traditional ground-based measurements to enhance model precision. The data undergoes processing to remove vegetation and structures, ensuring a smooth representation of the terrain.
Applications of DTMs
Digital Terrain Models support various industries, offering crucial data for numerous applications. In civil engineering, DTMs assist in road and infrastructure planning by analyzing elevation and slope stability. Environmental scientists rely on DTMs for watershed analysis, flood modeling, and erosion studies. Urban planners use DTMs to assess land suitability for construction, while archaeologists leverage them to detect ancient landforms hidden beneath vegetation. Additionally, DTMs play a vital role in agriculture, helping farmers optimize irrigation and soil management strategies.
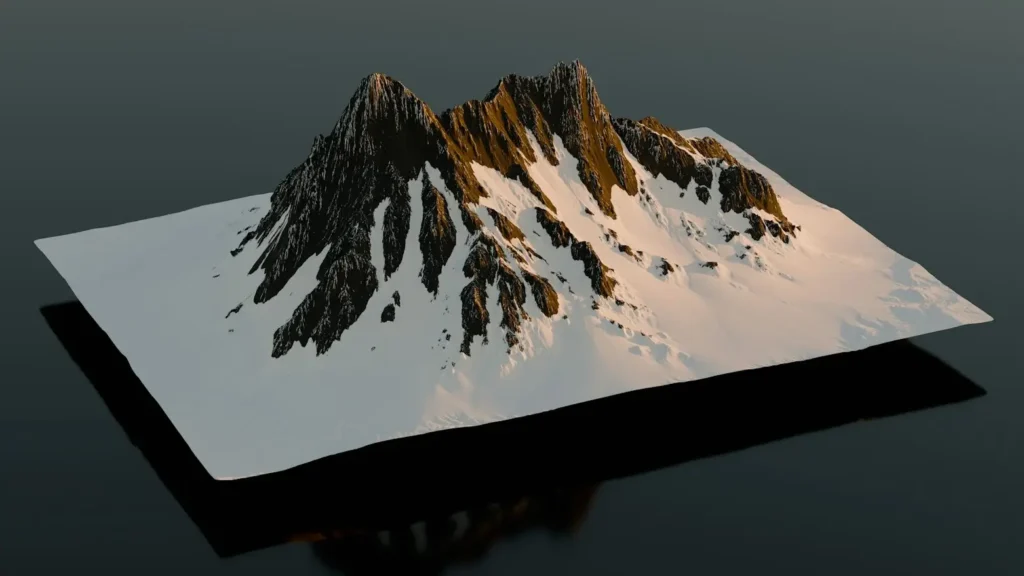

Advantages of Using DTM
DTMs provide exceptional accuracy for topographic analysis, ensuring reliable results in land surveying and engineering projects. Their ability to model terrain with precision makes them ideal for flood risk assessment and environmental impact studies. By offering detailed elevation insights, DTMs enhance decision-making in construction, forestry, and disaster management. The high level of detail in DTM aids in hydrological simulations, improving water resource management and ecological conservation efforts.
Challenges and Limitations of DTM
Despite their benefits, DTMs come with certain limitations. The accuracy of a DTM depends on the quality of data collection methods, with LiDAR offering higher precision than satellite-based models. Processing terrain data can be time-consuming, requiring sophisticated software and computational resources. Additionally, in areas with dense vegetation or complex landscapes, removing all above-ground features can pose challenges, leading to potential data inaccuracies.
Conclusion
Digital Terrain Models serve as indispensable tools in geospatial analysis, offering valuable insights across various industries. Their ability to provide a clear representation of the Earth’s surface enables better decision-making in engineering, environmental studies, and land management. As technology advances, DTMs will continue to play a pivotal role in mapping and analyzing the world’s landscapes, contributing to more efficient and sustainable development. If you want to be up to date with the next generation of geospatial data sharing, then keep in mind that DTMs and all the mentioned digital models can be uploaded, displayed and shared seamlessly via SurveyTransfer.
If you really liked what you read than you can share it with your friends. 🙂
Did you like what you read? Do you want to read similar ones?